As the blockchain market continues to evolve, the stories of Decred and Polygon highlight the efforts of two innovative communities
In 2017, the Matic Network was established in Mumbai by a group of visionary developers: Jayanti Kanani, Sandeep Nailwal, Anurag Arjun, and Mihailo Bjelic. Their primary objective was to tackle the scalability challenges facing the Ethereum blockchain. As the team began developing innovative solutions Matic Network quickly garnered attention and entered the investment spotlight. The project's unique approach to addressing Ethereum's network issues set it apart, attracting developers and investors to explore its potential.
In February 2021, the project went through a rebranding process and became Polygon Technology. Subsequently, in December 2021, Polygon made a significant move by acquiring the Mir blockchain network for 250 million MATIC tokens, valued at approximately $400 million during the deal. This strategic acquisition aimed to enhance Polygon's capabilities.
On the other hand, Decred was created to address the governance and scalability issues of Bitcoin. Decred was first discussed in 2013, when the Bitcointalk forum user tacotime, collaborated with another user known as _ingsoc, along with Jake Yocom-Piatt, to implement a hybrid Proof-of-Work (PoW) and Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus system. This collaborative effort resulted in the creation of a new project named Decred.
Both networks were developed to address the challenges of the two biggest blockchain networks. They introduced innovative solutions to overcome these issues. Let's analyze them and understand their operational mechanisms and features!
Operation
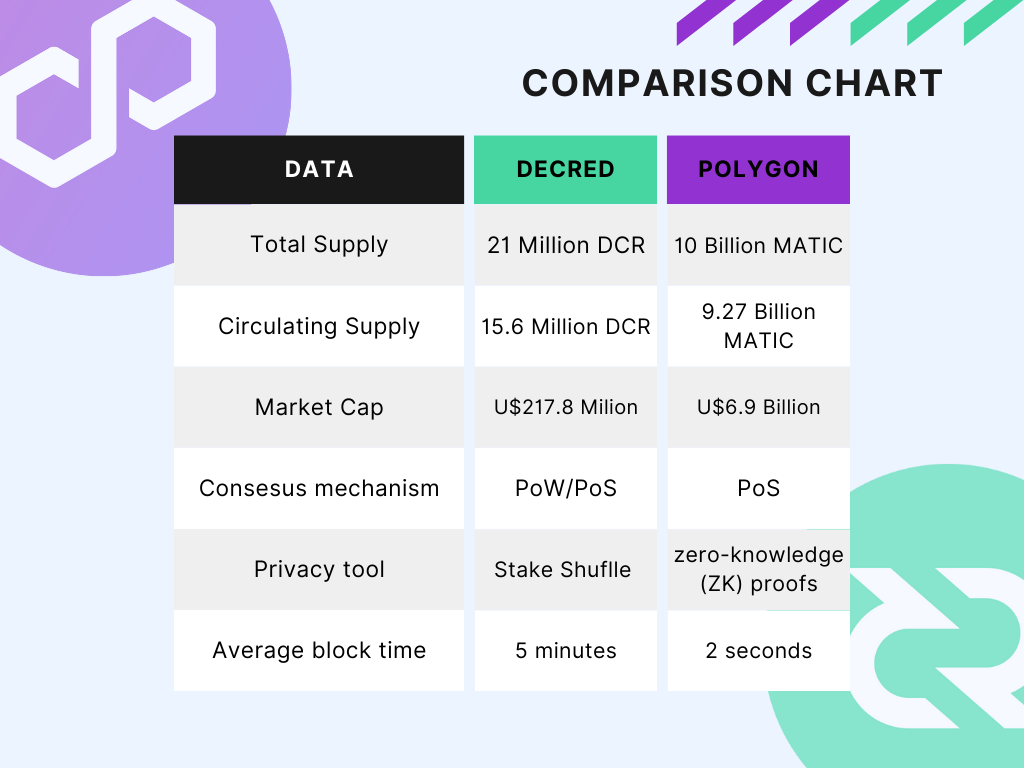
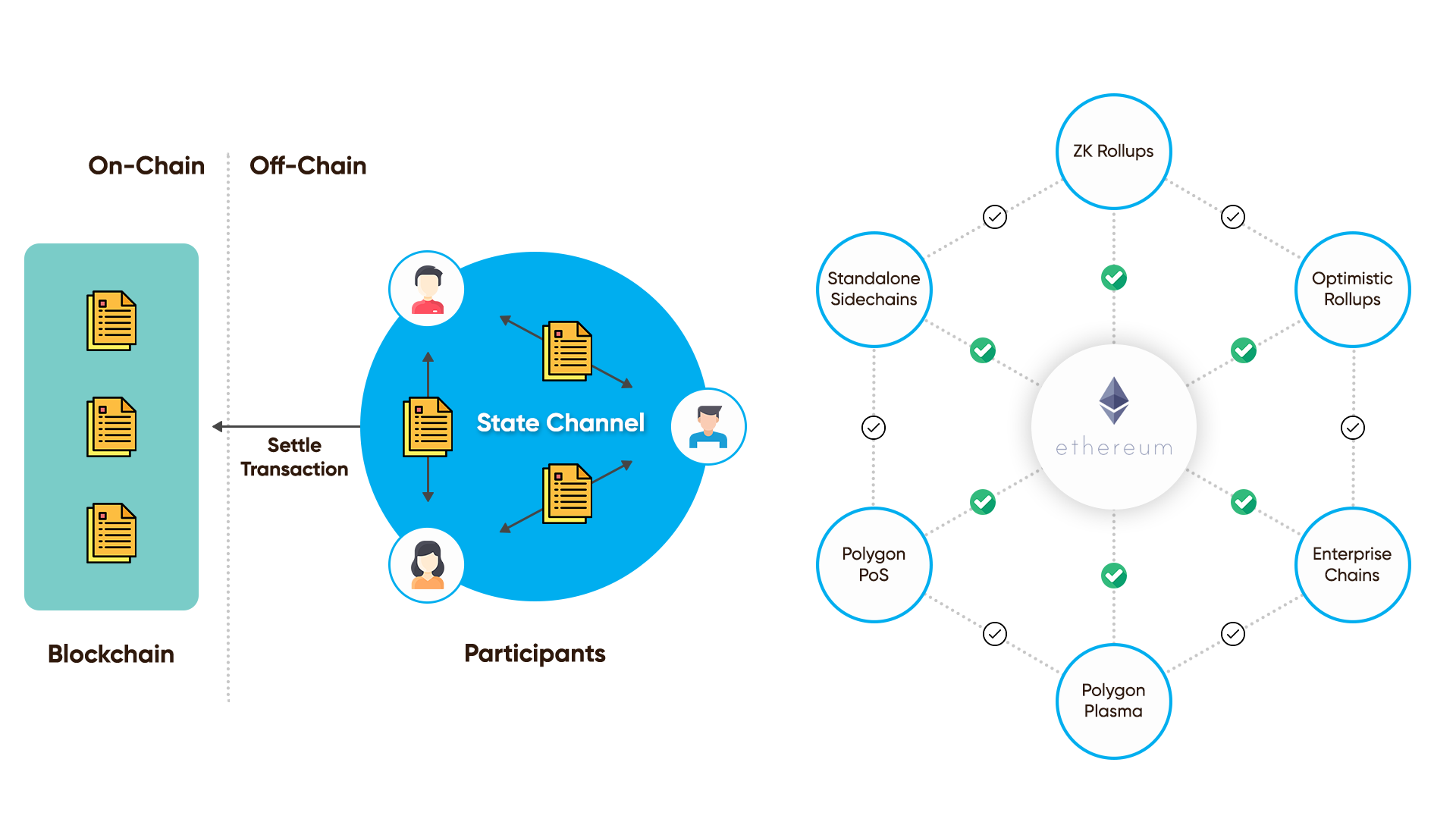
Polygon is an interesting network. It does not compete with Ethereum, but it relies on it. Polygon's Proof of Stake (PoS) blockchain serves as a Commit Chain linked to the Ethereum mainchain, attracting many Ethereum decentralized applications (dApps). These dApps operate on Polygon's platform, avoiding the network congestion commonly experienced on Ethereum and other Proof-of-Work (PoW) blockchains.
Decred's blockchain offers a layer of interoperability, much like Polygon's relationship with Ethereum. While Decred has its own blockchain, it doesn't compete directly with Bitcoin, instead, it complements its original concepts with innovations such as on-chain governance. Stakeholders can vote on Decred proposals to change/implement new features. Decreds hybrid PoW/PoS consensus presents a unique approach to security and decision-making. The use of Politeia, a proposal system, allows anyone to submit proposals for different types of projects, and the community votes if it's worth funding it.
On the other hand, the core of Polygon's functionality lies in Commit chains, which are transaction networks positioned alongside a primary blockchain, in this case, Ethereum. Commit chains bundle transactions into batches, confirming them collectively before sending data back to the main chain. The long-term vision for Polygon involves the integration of thousands of chains working in tandem to boost throughput, potentially reaching millions of transactions per second (TPS) when connected to a mainchain like Ethereum. While Polygon currently leverages Commit Chain connectivity to enhance transaction speed, it plans to incorporate other Layer-2 scaling mechanisms, such as Optimistic Rollups, in the future.
Great animation on how Polygon woks by WhiteBoard Crypto Youtube Channel
Funding
I was surprised to find out that Polygon also has a governance system like Decred. The project developed the Polygon Improvement Proposals (PIPs), which serve as comprehensive documents outlining standards within the Polygon ecosystem. They delineate the procedures by which the Polygon community suggests, reaches consensus on, and executes alterations to Polygon Protocols.
Authors utilize PIPs as a means to introduce and propose changes, capturing the community's sentiment on these proposals.
Additionally, PIPs function as a platform for authors to offer technical specifications and implementations for suggested upgrades. In essence, PIPs play a multifaceted role in facilitating the evolution of the Polygon network, encompassing proposal introduction, community feedback, and technical detailing of proposed enhancements.
As previously mentioned, Decred utilizes the Politeia platform for its proposal system. A key pillar of Decred's philosophy is sustainability, achieved through the allocation of 10% of block rewards to the Decred treasury. This reserved pool of DCR (Decred's native cryptocurrency) serves as a funding source for approved community proposals. The treasury funds a variety of initiatives, both development and marketing efforts, ensuring the continuous growth and advancement of the Decred project.
Transactions
As previously noted, Polygon tackles challenges faced by the Ethereum network. One of those issues is that the network can only perform a limited number of transactions per second. The base layer of Ethereum currently operates at a throughput rate of around 14 transactions per second. However, each transaction on Ethereum incurs gas fees, and during periods of high network congestion, these gas fees can escalate rapidly, reaching levels exceeding $50 to $80. This presents a significant barrier, rendering Ethereum less accessible for a majority of users.
The issue of exorbitant fees becomes especially pronounced for users engaging in decentralized finance (DeFi) activities, participating in the trade or purchase of nonfungible tokens (NFTs), or executing token swaps, buys, or transfers on the Ethereum network. The cumulative impact of these activities can result in substantial costs, discouraging users from actively participating in smart contracts and transactions on the Ethereum blockchain.
To reduce gas costs, Polygon executes transactions on side chains. The network handles up to 65.000 transactions per second. Transactions on the Ethereum network cost an average of U$15 per transaction, while Polygon charges its users just some pennies.
Decred maintains an average block time of roughly five minutes, accompanied by a block reward of approximately 16 DCR. The network undergoes a reward adjustment approximately every 21.33 days. On its main chain, Decred is capable of processing around 5-10 transactions per second. To enhance the scalability of the network, Decred implemented a Lightning Network (LN), which functions as a "Layer 2" protocol overlaying the base layer. This innovative protocol facilitates rapid, cost-effective transactions and achieves higher throughput by creating secondary, or off-chain, payment channels. In the LN transactions come with low cost and are completed almost instantly.
Another way to complete transactions on the Decred network is by using DCRDEX, Decred's decentralized exchange. With DCRDEX you don't have to worry about anyone profiting from your financial activity! All of your coins are under your full custody, and there are no arbitrary fees. Right now, the Polygon project stablecoin USDC is in the process of being listed on DCRDEX! Another good bridge between both projects.

Moving Foward
Polygon and Decred have walked parallel paths to address problems from the Ethereum and Bitcoin networks. Both projects demonstrate the importance of community involvement and transparent governance structures.
As the blockchain market continues to evolve, the stories of Decred and Polygon highlight the efforts of two brave communities. Those groups push the boundaries of innovation, collaboration, and decentralization. Did I miss anything about these projects? Or do you have any interesting thoughts to share about them? Leave a comment below!






Comments ()