The Governance Chronicles: Exploring Decred, Zcash, and Polygon in the Crypto Governance
It is evident that governance extends beyond technical intricacies, offering a nuanced dance of community dynamics and shared principles.


Governance stands as one of the main differentials in the crypto industry, providing the essential framework that underpins the viability, adaptability, and integrity of blockchain networks. Beyond mere technical prowess, governance mechanisms serve as a mirror to community values, forming a crucial social contract among participants.
Governance plays a crucial role in the world of cryptocurrency, aligning with the core principle of decentralization. Projects that dedicate efforts to refine their governance structures serve as models not just for traditional companies but also for governments. They emphasize the importance of member participation and underscore the ongoing possibilities for improvement in fostering inclusive decision-making processes.
In the Decred, Zcash, and Polygon projects, governance systems play a main role in shaping how protocol changes, encompassing upgrades and feature additions, are deliberated upon and executed. These systems are the bedrock that ensures the seamless integration of emerging technologies, safeguarding against disruptions that could compromise the network and its user base. Let's analyze those projects and check how they contribute to modernizing the idea of governance and member participation.
The examination of governance across Decred, Zcash, and Polygon unveils not just the technical intricacies but also the intricate dance of community dynamics and shared principles that propel these cryptocurrencies forward.
Decred
Decred has been designed to undermine the concentration of influence in the hands of powerful individuals or central planning committees when determining the project's future trajectory. Instead, the governance structure of Decred revolves around the innovative concept of ticket-holder voting. Proposed alterations to the system undergo a voting process, with implementation contingent on the approval of the voters. Individuals holding a sufficient amount of DCR have the option to time-lock their coins, enabling them to purchase tickets and actively participate in the governance process.
As Jake Yocom-Piatt, the Decred project leader, succinctly puts it:
"Decred cryptocurrency governance is as low complexity as possible, with the constraint of remaining sustainable over a multi-decade timescale. Most cryptocurrency governance systems depend on high complexity smart contracts and do not operate at Layer 1/on-chain. In many cases, other cryptocurrencies' governance decisions are not binding and are only a form of soft signaling. Decred consensus changes and treasury spending transactions require direct on-chain approval by a supermajority of stake, and proposals require off-chain approval by a supermajority of stake."
This quote encapsulates Decred's commitment to simplicity, sustainability, and on-chain governance, which stands in contrast to the intricate smart contract-dependent systems of other cryptocurrencies.

the governance procedures within Decred can be divided into two main topics: On-chain Voting and Off-chain Voting through the Politeia Platform.
On-chain Voting:
- Block Validation:
- On-chain voting is utilized for the essential process of validating blocks within the Decred blockchain.
- Stakeholders participate in voting to determine the acceptance or rejection of proposed blocks, contributing to the security and integrity of the blockchain.
- Consensus Rule Changes:
- On-chain voting is employed to make decisions on proposed consensus rule changes.
- Stakeholders can cast votes on protocol upgrades, ensuring a decentralized approach to evolving the Decred network.
Off-chain Voting through Politeia Platform:
- Treasury Fund Allocation:
- Decisions related to the allocation of Treasury funds are conducted through off-chain voting on the Politeia platform.
- Stakeholders can participate in discussions and cast votes on proposals for allocating funds to various projects, initiatives, or development efforts.
- Policy Changes and Amendments:
- Off-chain voting extends to higher-level issues, such as amendments to the Decred constitution or significant policy changes.
- The Politeia platform serves as a forum for stakeholders to engage in discussions, propose changes, and vote on decisions that impact the broader governance structure and policies of Decred.
- Community Engagement:
- The Politeia platform enables off-chain discussions and engagement, providing a space for stakeholders to voice their opinions on various governance matters.
- Decisions made through Politeia are reflective of the collective sentiment of the Decred community.
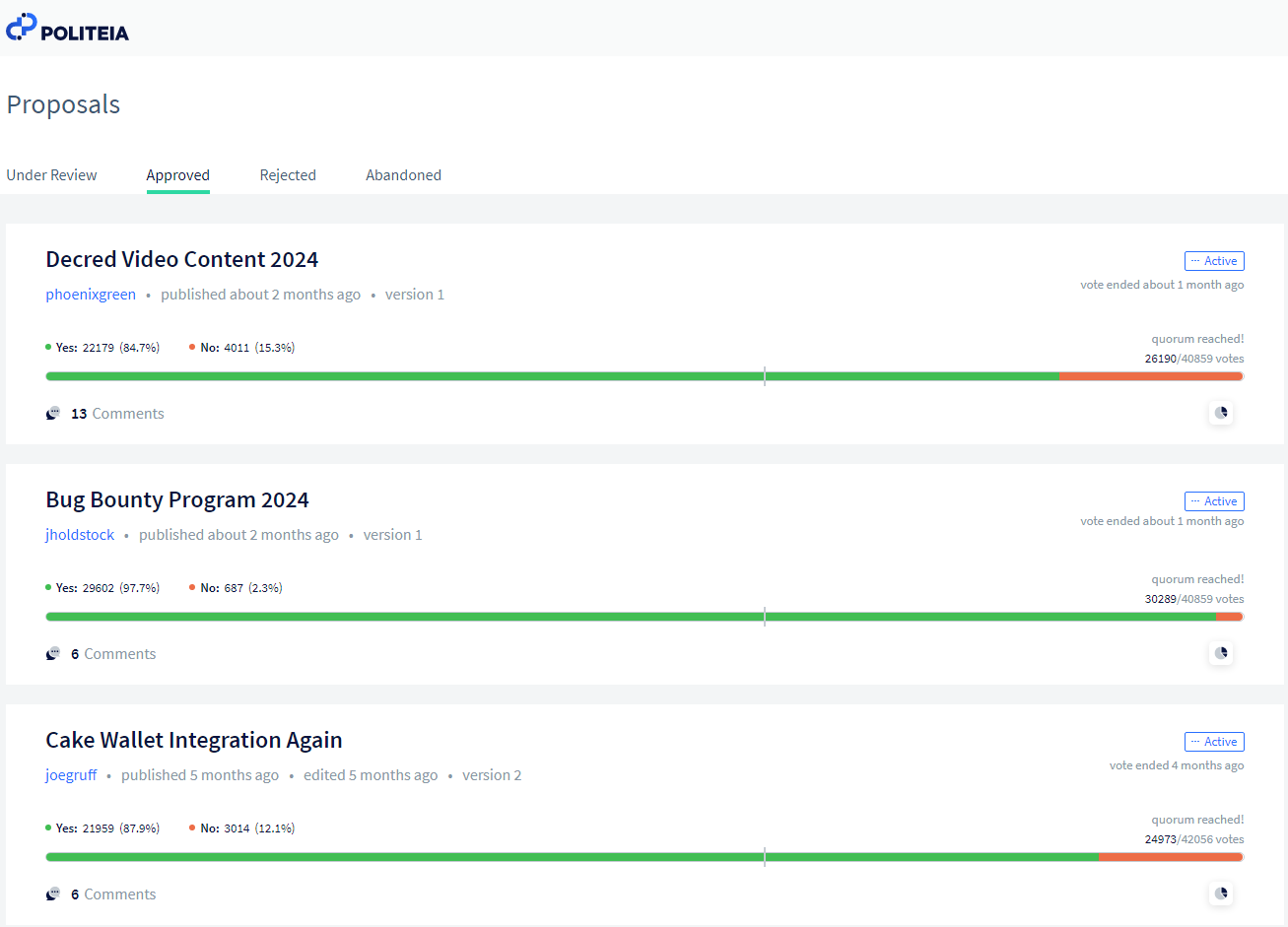
Decred's governance model stands out as a comprehensive and adaptive framework that blends on-chain and off-chain voting mechanisms. The integration of on-chain voting for critical protocol decisions and off-chain voting through the Politeia platform for higher-level governance matters ensures a delicate balance between technical advancements and broader community-driven initiatives/debates. The great advantage of the Politeia platform is the way that it centralizes proposals, discussions, and voting in one single place.
The adaptability of Decred's hybrid nature is a key perk, allowing the network to navigate changes efficiently. On-chain voting validates transactions and protocol upgrades, addressing technical aspects, while off-chain voting on Politeia provides the flexibility needed for community-driven decisions and resource allocation. This dynamic governance model positions Decred as a resilient and evolving decentralized platform, capable of responding effectively to the ever-changing landscape of blockchain technology and community needs.
Zcash
Zcash is one of the most notorious privacy coins in the market, its community has developed a governance system that allows members to participate and open debate. In November 2019, a significant milestone marked Zcash's journey when the Electric Coin Co. generously donated the Zcash trademark to the Zcash Foundation. This move was made under an agreement emphasizing mutual consensus on network upgrades, underscoring Zcash's commitment to community input and ensuring decisions align with the clear consensus of the Zcash community.
Zcash's governance framework is rooted in decentralization and community-driven decision-making. The Zcash Foundation, a key player in this ecosystem, actively manages official discussion forums and polling systems. These platforms serve as vital spaces for engaging the diverse Zcash community, ensuring that the collective voice is not only heard but considered in decision-making processes.
The Zcash project developed Zcash Improvement Proposals (ZIPs) to establish a structured and transparent process for proposing, discussing, and implementing changes or enhancements to the Zcash cryptocurrency ecosystem.
The process of introducing a new enhancement or feature to Zcash through the Zcash Improvement Proposal (ZIP) system is a structured and collaborative journey. It commences with the conceptualization of a novel idea, with the individual or group proposing the idea assuming the role of Owners for the ZIP. Following this, Owners engage with the Zcash community on the Zcash Community Forum, actively seeking input and feedback to gauge the viability and acceptance of the proposed feature.
Upon thorough community discussion, Owners proceed to draft a ZIP document that encapsulates a concise technical specification and budget of the proposed enhancement. This document is crucial in providing clarity on the rationale behind the feature. Subsequently, the draft ZIP is presented on the Zcash Community Forum, initiating a phase of additional discussion and feedback collection. Owners meticulously consider community input, addressing concerns, and refining the proposal based on the feedback received. Once the ZIP draft has undergone thorough examination and refinement, Owners submit it as a pull request to the ZIPs git repository.
ZIP Editors play a pivotal role in the subsequent stages, conducting a comprehensive review to ensure the readiness, soundness, and completeness of the ZIP. The ZIP undergoes revisions and further review cycles until it is deemed ready for approval by the editors. The final step involves removing the Draft status and merging the pull request into the ZIPs git repository, signifying the official approval of the ZIP. This approved ZIP becomes part of the historical record, and ongoing monitoring and updates are conducted by ZIP Editors and Owners to ensure the maintenance and improvement of the feature within the Zcash ecosystem.
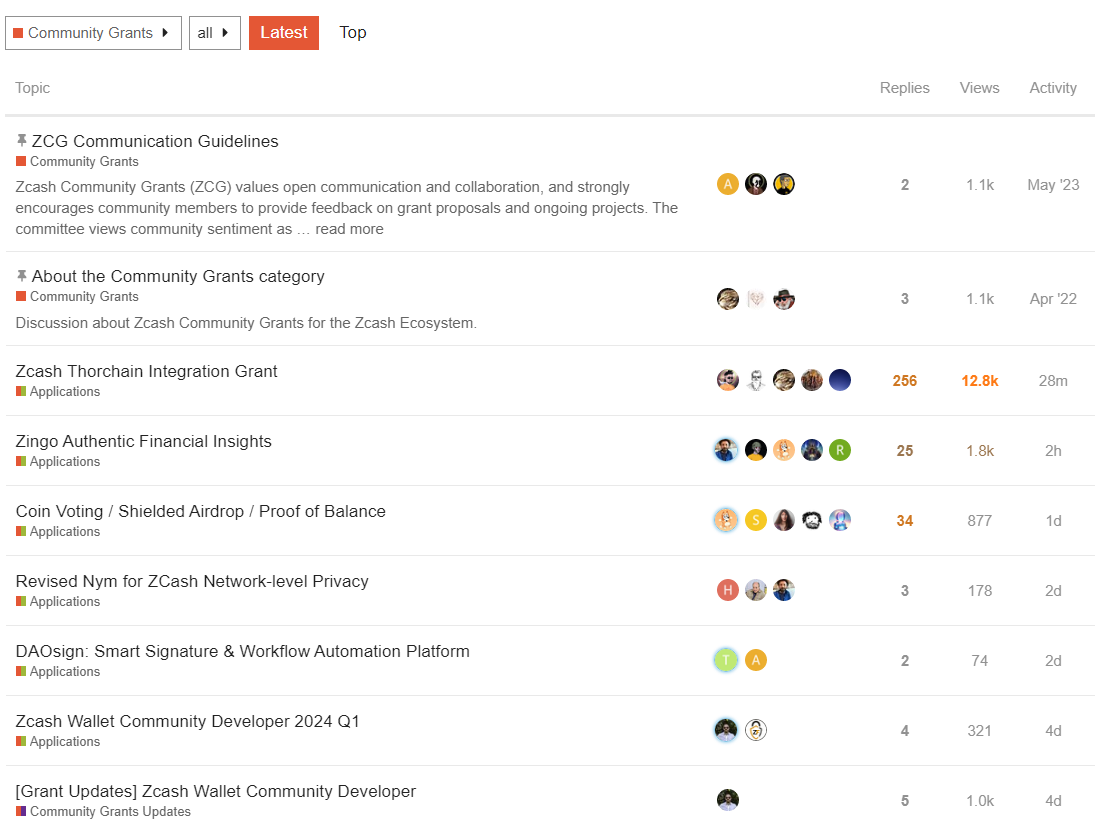
Check out how the Zcash community votes and check ZIPs accountability on the Zcash community forum:
Zcash Thorchain Integration Grant
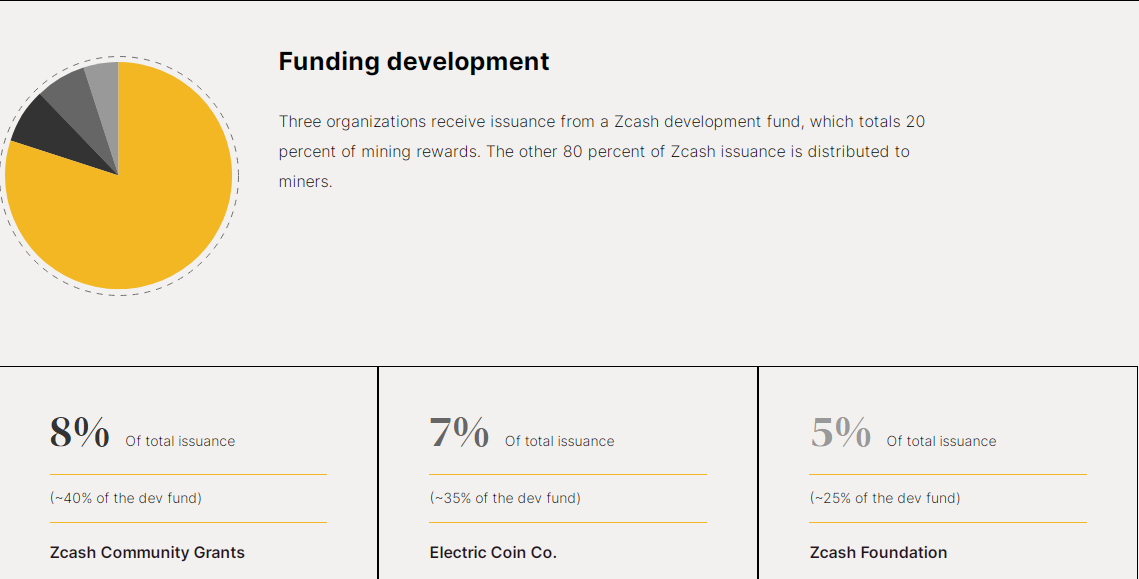
Three organizations receive issuance from a Zcash development fund, which is composed of 20 percent of mining rewards. The other 80 percent of Zcash issuance is distributed to miners for their part in securing the network as follows:
- Zcash Community Grants (formerly ZOMG):
- Allocation: 8% of total issuance (~40% of the dev fund)
- Purpose: Zcash Community Grants serves as a platform for distributing funding to independent, third-party developers engaged in Zcash-related projects. This initiative plays a crucial role in supporting external contributors and fostering innovation within the Zcash ecosystem. The Zcash Community Grants is administered by the Zcash Foundation.
- Electric Coin Co. (ECC):
- Allocation: 7% of total issuance (~35% of the dev fund)
- Role: ECC, a subsidiary of the nonprofit Bootstrap Project, spearheaded the launch of Zcash in 2016 and continues to provide steadfast support. ECC contributes to the Zcash ecosystem through research and development (R&D), engineering efforts, regulatory relations, and activities focused on adoption and demand generation.
- Zcash Foundation:
- Allocation: 5% of total issuance (~25% of the dev fund)
- Mission: The Zcash Foundation, operating as a public charity, is dedicated to building financial privacy infrastructure for the greater public good. It primarily serves users of the Zcash protocol and blockchain. The foundation's commitment to advancing financial privacy aligns with its status as a nonprofit organization, emphasizing its focus on benefiting the broader community.
Zcash has effectively implemented a governance model that enables community-wide discussions on proposals through the Zcash forum. This process is deliberately structured to be open and transparent, ensuring accessibility for all members. However, concerns have emerged regarding the potential concentration of power within the Zcash Foundation and Electric Coin Company. The ZIP editors, who hold the responsibility of approving or rejecting a ZIP, currently consist of members from both the Zcash Foundation and Electric Coin Company. This composition has sparked apprehensions about the significant influence wielded by these corporations in the decision-making process.
In response to these concerns, some community members are exploring the idea of dissolving existing trademarks associated with Zcash. The objective is to establish a new, non-U.S.-based organization that would assume control of the project's governance. This proposal seeks to address perceived issues related to centralization and aims to foster a more inclusive and globally distributed approach to decision-making within the Zcash ecosystem. You can check this discussion here!
Polygon
Polygon (MATIC) serves as a stack of protocols strategically crafted to tackle Ethereum's scalability concerns. The network effectively addresses these challenges by managing transactions on a distinct Ethereum-compatible blockchain.
Polygon employs a governance system similar to the Zcash one, featuring the establishment of Polygon Improvement Proposals (PIPs). Anyone within the Polygon community can create a PIP. These proposals serve as comprehensive documents that articulate the standards governing the Polygon ecosystem. PIPs delineate the processes through which the Polygon community suggests, achieves consensus on, and implements changes to Polygon Protocols.
Authors leverage PIPs as a mechanism to introduce and advocate for modifications, capturing the sentiments of the community regarding these proposals.
Moreover, PIPs serve as a platform for authors to present technical specifications and implementations for suggested upgrades. In essence, PIPs play a versatile role in facilitating the evolution of the Polygon network, encompassing the introduction of proposals, community feedback, and the technical detailing of proposed enhancements. All of Polygon's PIPs are discussed in the Polygon Community Forum.
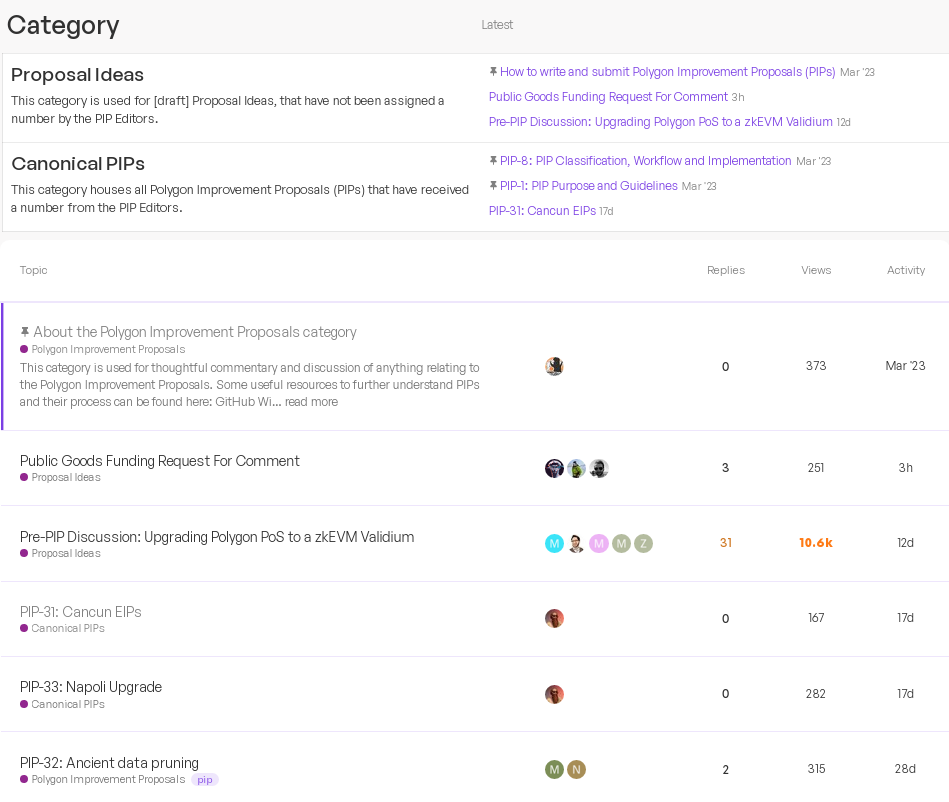
The approval process for a Polygon Improvement Proposal (PIP) involves several stages of community engagement and review. Here is a general outline of how a PIP is approved within the Polygon ecosystem:
- Proposal Submission:
- Any member of the Polygon community can propose a PIP by publishing it on the Polygon Community Forum.
- Pull Request and Review:
- The proposal is then turned into a pull request on the official Polygon repository.
- A PIP editor reviews the proposal, assigns a number, and suggests changes if necessary.
- Peer Review and Community Discussion:
- The PIP undergoes peer review, with the community discussing its merits and potential drawbacks.
- Polygon Builder Sessions may be held to communicate the proposal to a larger audience.
- Last Call:
- Editors assign a 'Last Call' status to the PIP, signaling the final opportunity for community feedback.
- This status remains for 14 days to collect additional feedback.
- Final Decision:
- After considering all feedback, the PIP editors make a final decision on whether to approve or reject the proposal.
- If approved, the PIP is marked as accepted and moves to the implementation phase.
- Implementation:
- The developer team starts prioritizing and implementing the accepted PIP.
- This involves coding the proposed changes and integrating them into the Polygon protocol.
- Execution and Deployment:
- Once the implementation is complete, the changes are executed, and the updated protocol is deployed on the Polygon network.
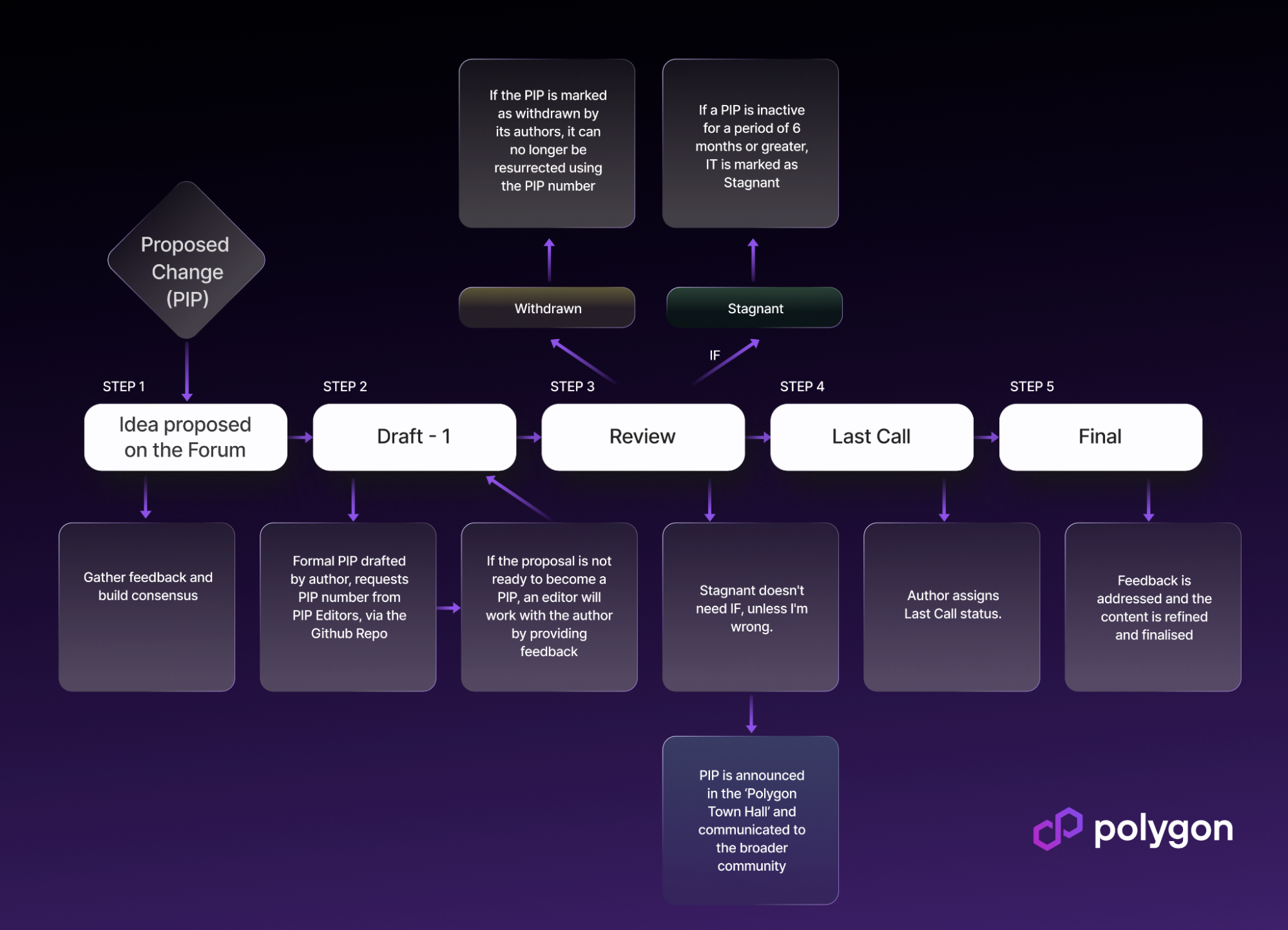
specific improvements, as identified by its community members. Presently, the process of proposing a Polygon Improvement Proposal (PIP) involves navigating across multiple platforms. Validators engage in discussions on the forum and cast votes on the Validators channel on Discord, resulting in a somewhat slow and complex procedure. In contrast to proposals in projects like Zcash and Decred, Polygon PIPs lack a specified budget within the proposal, creating uncertainty regarding how the initiative will be funded.
Members within the Polygon community have proposed streamlining and centralizing the decision-making process onto a single platform to enhance consistency and simplify navigation. To address this, the community has experimented with the use of the snapshot voting platform for certain decisions. In this approach, validators can cast votes using their Owner addresses, adhering to a 1 address = 1 vote principle, mirroring the off-chain consensus reached within the validator community.
However, a notable challenge arises as any potential solution aiming to consolidate all decision-making processes onto a single platform would require the DAO to deviate from its existing setup and embrace a new framework. This shift would necessitate careful consideration and planning to ensure a smooth transition while maintaining the integrity and effectiveness of the decentralized autonomous organization (DAO).
Moving Forward
In conclusion, governance emerges as a pivotal differentiator in the cryptocurrency industry, serving as the backbone for the viability, adaptability, and integrity of blockchain networks. Beyond its technical dimensions, governance reflects community values and establishes a vital social contract among participants.
Decred, Zcash, and Polygon showcase diverse approaches to governance, each contributing to the modernization of decentralized decision-making and member participation.
Decred's innovative ticket-holder voting system disrupts traditional power structures, offering a comprehensive blend of on-chain and off-chain mechanisms. This hybrid model allows for efficient validation of transactions and protocol upgrades, while also facilitating community-driven decisions and resource allocation through the Politeia platform.
Zcash, known for its privacy-focused features, also places a strong emphasis on community input. The Zcash Foundation actively manages discussion forums and polling systems, ensuring that decisions align with the consensus of the diverse Zcash community. The governance structure also a clear allocation of funds to community grants, the Electric Coin Co., and the Zcash Foundation.
Polygon addresses Ethereum's scalability challenges with a user-friendly framework. The Polygon Improvement Proposals (PIPs) provide a structured process for introducing, discussing, and implementing changes, although ongoing discussions about centralizing the proposal process highlight a desire for improvement.
In examining these projects, it is evident that governance extends beyond technical intricacies, offering a nuanced dance of community dynamics and shared principles. These cryptocurrencies exemplify the evolution of governance models, contributing to the ongoing narrative of decentralized decision-making in the crypto space.





Comments ()